Isi Kandungan Artikel
What SPF Level is Best for You?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It measures the level of UV radiation protection and ranges from 1 – 90.
The SPF indicates the length of time that your skin is protected from sunburn, depending on your skin type. To help you understand a bit better, if you start getting sunburned after five minutes in the sun without any sunscreen, applying a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 would protect you for 30 x 5 minutes (or 150 minutes or 2.5 hours) before you begin to burn. Depending on your skin type, the time it takes for you to begin getting burned is between 5 to 30 minutes, on average.
There are some other factors that will also affect your level of protection, such as:
- How much sunscreen you apply
- The weather conditions
- How much you sweat
- How long you swim
- Your skin type
What is UV radiation and the difference between UVA, UVB and UVC ?
The sun emits three different types of UV radiation: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
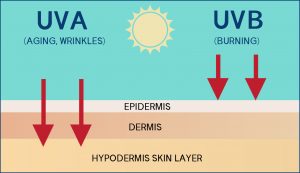
All types of UV radiation have the potential to damage your skin, but each type affects your skin differently. UVA rays, which account for 95 percent of radiation that reaches the earth’s surface, cause wrinkles, “sun spots,” and other types of premature aging. They are also strongly linked to skin cancer. For our beauty, it speeds up skin aging ( wrinkles, lines, and saggy skin) and can also cause hyperpigmentation. UVA radiation, which accounts for most of the sun’s rays, penetrates into the deeper levels of skin and is present all through the day, even on cloudy days. An easy way to remember? UVA, UV-Aging.
UVB rays, which affect skin’s top layer, cause skin cancer and most sunburns. UVB energy causes redness and sunburn on the skin. Want a trick to remember this? Repeat with us: UVB, UV-Burn!
Although UVA and UVB rays pose the greatest risk for sun damage, people who work with welding torches or mercury lamps may be exposed to UVC rays, the most dangerous type of UV radiation.
With so many different sun protection levels out there, it can be hard to figure out what’s right for you. Is there really a difference between SPF 30 and 50?
Why do we have different SPF levels — why don’t we just have one standard?
Darker skin types can use a lower level, such as SPF15, since they have more melanin in their skin, which does give some protection. Darker skin may not sunburn as easily as those with fair skin, but they are still at risk of skin damage from sun exposure.
SPF 30 is the most common level for most people and skin types. No sunscreen can block all UV rays, but what we do know is:
- SPF 15 blocks 93% of UVB rays,
- SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays,
- SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays.
So, the difference between 30 and 50 is about 1 percent. But every bit of extra protection can be beneficial if you are very fair or spending a lot of time in direct sun!
Are there any drawbacks to using a higher SPF?
There is often a false sense of security with higher numbers. You think since you’re wearing a higher level, you are invincible to the sun, and that’s just not the case. Most of us also forget that SPF is only at its most active for about two hours, so you need to reapply it often.
Does the product texture change as you move higher up in SPF level? How does it impact the look and feel of it?
The product texture can change, but it’s not very noticeable. It’s more about the types of sunscreens ingredients used. Physical sunscreens made with titanium dioxide or zinc oxide will usually be slightly more opaque then chemical sunscreens. But many sunscreens products now combine several different active chemical and physical sunscreen ingredients in order to provide broad-spectrum protection.






